Vectors and Matrices in Visual Basic
Vectors and matrices are core concepts in linear algebra and play a central role in many Visual Basic applications, particularly in graphics, animation, simulations, and game development. Understanding how to represent and manipulate vectors and matrices in Visual Basic provides a strong mathematical foundation for working with coordinate systems, transformations, and motion in two and three dimensions.
This page introduces vectors and matrices in Visual Basic and demonstrates how common vector and matrix operations can be implemented directly in code. The emphasis is on clarity and mathematical correctness rather than reliance on external libraries, making the techniques suitable for learning and educational use.
Understanding Vectors and Matrix Operations in Visual Basic
In programming, a matrix is often represented as an "array within an array." Mastery of Visual Basic matrix operations allows you to perform rotations, scaling, and translations in 2D and 3D space programmatically.
Defining Your Data Structures
To begin, we represent our mathematical objects as standard Visual Basic arrays. A vector is treated as a specific type of matrix—one with a single column.
- Scalar: A single numerical value.
- Vector: A list of numbers representing magnitude and direction.
- Matrix: A rectangular grid of numbers arranged in rows and columns.
Representing Vectors in Visual Basic
In Visual Basic, vectors are commonly represented using arrays or simple objects. A vector may describe a position, displacement, velocity, or direction, depending on the context in which it is used.
For example, a two-dimensional vector can be stored as an array containing its components along the x- and y-axes. This representation allows standard vector operations in Visual Basic, such as addition, subtraction, and scaling, to be implemented using straightforward functions.
Working with vectors in this way helps reinforce the connection between linear algebra concepts and practical Visual Basic programming.
Vector Operations in Visual Basic
Basic vector operations form the foundation for more advanced mathematical techniques used in graphics and animation.
Common vector operations include:
- Vector addition and subtraction
- Scalar multiplication
- Calculating magnitude (length)
- Normalising a vector
Implementing these vector operations in Visual Basic allows programmers to model motion, forces, and directional changes accurately. These techniques are especially useful in canvas-based graphics and interactive applications where precise control over movement is required.
Representing Matrices in Visual Basic
Matrices extend vector ideas and are essential for handling transformations such as rotation, scaling, and translation. In Visual Basic, matrices are typically represented as two-dimensional arrays, where each inner array corresponds to a row of the matrix.
This approach closely mirrors the mathematical definition of a matrix and makes it easier to translate linear algebra formulas directly into Visual Basic code. It also prepares students for more advanced topics such as matrix multiplication and coordinate transformations.
Matrix Operations in Visual Basic
Matrix operations in Visual Basic allow complex transformations to be expressed concisely and applied consistently.
Typical matrix operations include:
- Matrix addition and subtraction
- Matrix multiplication
- Multiplying a matrix by a vector
- Calculating determinants and inverses (for square matrices)
Since matrices can be represented as arrays of arrays. With Visual Basic, you can easily perform:
- Matrix Addition and Subtraction - Combine or reduce values element by element.
- Matrix Multiplication - Essential for scaling, rotating, and skewing objects in graphics.
- Determinant and Inverse Matrix - Useful for solving systems of equations and advanced transformations.
Example: Visual Basic Algorithm for Multiplication of Matrices >>>
These matrix operations are central to linear algebra and are widely used in computer graphics, physics simulations, and game engines. Implementing them manually in Visual Basic strengthens understanding of both the mathematics and the underlying algorithms.
Vectors as Matrices
Vectors can be treated as single-row or single-column matrices. This makes it easy to apply linear algebra techniques in Visual Basic:
- Representing points in 2D and 3D space.
- Performing dot products and cross products.
- Applying transformations for animations and simulations.
Image Manipulation with Matrices
Beyond math, matrices are widely used in Visual Basic image manipulation. By applying matrix operations, you can:
- Rotate images clockwise or counterclockwise.
- Scale pictures up or down.
- Skew and mirror graphics for creative effects.
- Combine with HTML Canvas or SVG graphics for dynamic rendering.
Using Vectors and Matrices for Graphics
Vectors and matrices are particularly important in web graphics, including HTML5 canvas and SVG. Vectors can represent positions and directions, while matrices are used to apply transformations such as rotation, scaling, and reflection.
For example, a transformation matrix can be used to rotate a shape about the origin or scale an object uniformly across the screen. Combining vector and matrix techniques allows complex graphical effects to be achieved using relatively simple Visual Basic code.
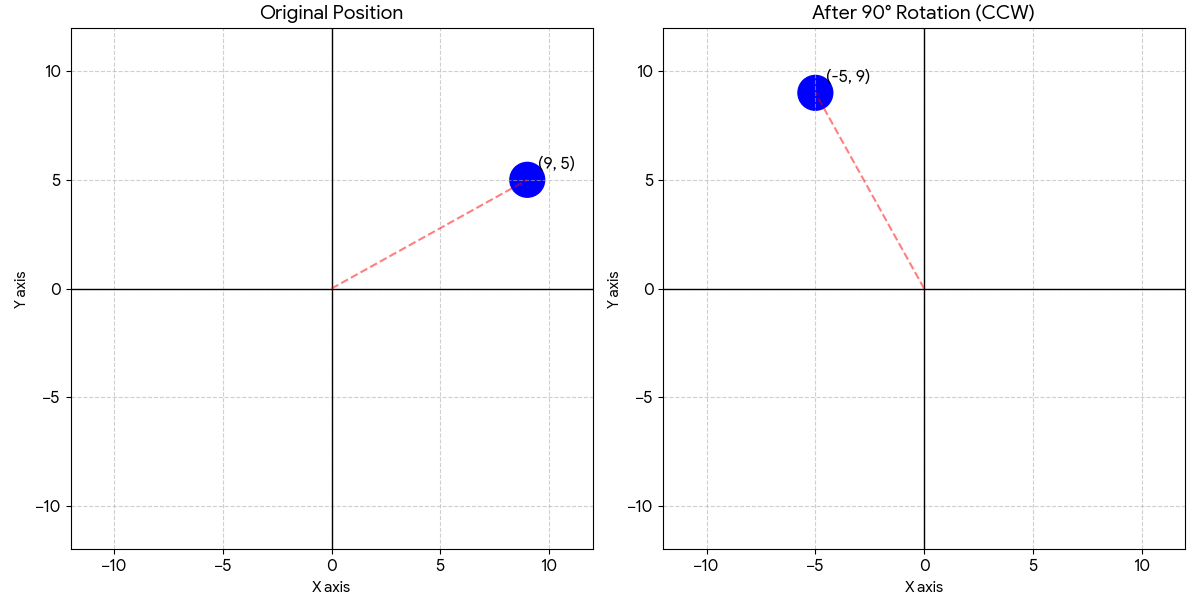
Example: Visual Basic Algorithm for rotation of vectors using a rotation matrix on a 2D plane >>>
Understanding these ideas also provides a solid introduction to the mathematics behind animation, game development, and computer graphics more generally.
Educational Focus and Further Study
The methods presented here are intended for educational use at a tertiary level. By coding vectors and matrices directly in Visual Basic, students gain a deeper appreciation of linear algebra concepts and how they are applied in real programming contexts.
An obvious improvement and practice exercise or fun activity is including checks in the Visual Basic algorithm to make sure the supplied matrices meet the dimensional requirement for matrix multiplication.
Once these fundamentals are understood, learners can more confidently move on to advanced topics such as transformation pipelines, three-dimensional graphics, and specialised Visual Basic libraries that build upon the same mathematical principles.
Practical Applications
- Web Development: Enhance animations and transitions with matrix transformations.
- Game Design: Use vectors and matrices for physics simulations and character movement.
- Educational Projects: Build interactive math tutorials and visualizations.
Summary: Vectors and Matrices in Visual Basic
Vectors and matrices are fundamental tools in mathematics and computer science. In Visual Basic, they provide a powerful way to perform matrix operations and vector calculations that support everything from graphics transformations to image manipulation. This tutorial explored how to implement matrix addition, subtraction, multiplication, determinants, and inverses directly in Visual Basic.
- Vectors and matrices are fundamental tools in Visual Basic programming for graphics and simulations
- Visual Basic arrays provide a clear and effective way to represent vectors and matrices
- Implementing vector and matrix operations reinforces linear algebra concepts
- These techniques form the mathematical basis of canvas graphics, animation, and game development
Mastering vectors and matrices in Visual Basic opens the door to advanced graphics transformations, image manipulation, and mathematical problem solving. Whether you’re a student learning linear algebra or a developer building interactive web applications, these concepts are essential for creating dynamic, visually engaging projects.
VB.Net Code for Multiplication of Matrices - Class File
' Matrix multiplication in JavaScript
' Follows same steps as you would do on paper
'
' Warning: No checks have been done To ensure the
' dimension of both matrices are in order for multiplication
'
Public Function multiplyMatrices(a As List(Of List(Of Double)), b As List(Of List(Of Double))) As List(Of List(Of Double))
Dim result As New List(Of List(Of Double))
For i As Integer = 0 To a.Count - 1
Dim row_values As New List(Of Double)
For j As Integer = 0 To b(0).Count - 1
Dim sum As Double = 0
For k As Integer = 0 To b.Count - 1
sum += a(i)(k) * b(k)(j)
Next k
row_values.Add(sum)
Next j
result.Add(row_values)
Next i
Return result
End Function
End Class
VB.Net Code for Multiplication of Matrices - Main Module
Module Program
Sub Main(args As String())
Dim matrix_A As New List(Of List(Of Double))({
New List(Of Double)({5, 0, 2}),
New List(Of Double)({1, 3, 8}),
New List(Of Double)({6, 1, 4})
})
Dim matrix_B As New List(Of List(Of Double))({
New List(Of Double)({2, 0, 0}),
New List(Of Double)({0, 2, 0}),
New List(Of Double)({0, 0, 2})
})
Dim mul_mat As New MultiplyMatrix
Dim result As List(Of List(Of Double)) = mul_mat.multiplyMatrices(matrix_A, matrix_B)
' print style inherently assumes same dimension for matrices A, B And result
Dim print_result As String = "[ "
print_result &= " "
print_result &= "[ "
print_result &= " ["
Dim rows_centre As Integer = Math.Ceiling(result.Count / 2) - 1
For i As Integer = 0 To result.Count - 1
print_result &= Environment.NewLine & " [" & String.Join(", ", matrix_A(i)) & "]"
If i = rows_centre Then
print_result &= " X "
Else
print_result &= " "
End If
print_result &= " [" & String.Join(", ", matrix_B(i)) & "]"
If i = rows_centre Then
print_result &= " = "
Else
print_result &= " "
End If
print_result &= " [" & String.Join(", ", result(i)) & "]"
Next i
print_result &= Environment.NewLine & "] "
print_result &= " "
print_result &= "] "
print_result &= " ]"
Console.WriteLine(print_result)
End Sub
End Module
VB.Net Code for Rotation of Matrices - Class File
Inherits MultiplyMatrix
' Matrix rotation in Visual Basic
Public Function rotateAMatrix(matrix As List(Of List(Of Double)), angle As Double) As List(Of List(Of Double))
Dim angle_in_radians As Double = angle * (Math.PI / 180)
' 3D rotation matrix - the extra zeroes (0) And ones (1) are there for unity matrix balance
Dim rotation_matrix As New List(Of List(Of Double))({
New List(Of Double)({Math.Cos(angle_in_radians), -Math.Sin(angle_in_radians), 0, 0}),
New List(Of Double)({Math.Sin(angle_in_radians), Math.Cos(angle_in_radians), 0, 0}),
New List(Of Double)({0, 0, 1, 0}),
New List(Of Double)({0, 0, 0, 1})
})
Return multiplyMatrices(rotation_matrix, matrix)
End Function
End Class
VB.Net Code for Rotation of Matrices - Main Module
Imports System.Reflection.Metadata
Module Program
Sub Main(args As String())
Dim vector_A As New List(Of List(Of Double))({
New List(Of Double)({9}), ' x-coordinate
New List(Of Double)({5}), ' y-coordinate
New List(Of Double)({0}), ' z-coordinate - use zero(0) for 2D special systems
New List(Of Double)({1}) ' balance for 4x4 rotation matrix
})
Dim angle As Double = -90
Dim rot_mat As New RotateMatrix
Dim result As List(Of List(Of Double)) = rot_mat.rotateAMatrix(vector_A, angle)
' do a formatted print style
Dim spacing_span As String = " "
spacing_span &= " "
Dim spacing As String = spacing_span
Dim print_result As String = spacing
print_result &= "[ [" & Environment.NewLine
Dim rows_centre As Integer = Math.Ceiling(result.Count / 2) - 1
For i As Integer = 0 To result.Count - 1
If i = rows_centre Then
print_result &= "A " & angle & " rotation of "
spacing = " "
Else
spacing = spacing_span
End If
print_result &= spacing & " [" & String.Join(", ", vector_A(i)) & "]"
If i = rows_centre Then
print_result &= " = "
Else
print_result &= " "
End If
print_result &= " [" & String.Join(", ", result(i)) & "]" & Environment.NewLine
Next i
print_result &= spacing
print_result &= "] ]"
Console.WriteLine(print_result)
End Sub
End Module