Code for Doing Combination in Java
Writing up an algorithm to carry out the different Combination - Selection without Repetition, nCr - of a set of things in Java requires some level of imaginative thinking.
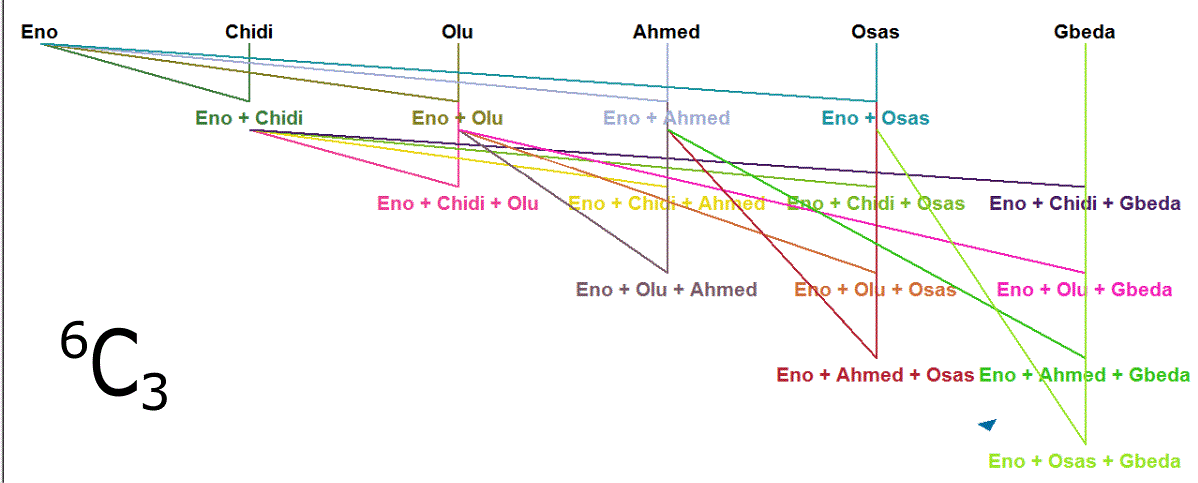
Get a writing pad and pencil:- Write out all n members in the set - for Combination - at the top of the pad.
- Beginning with the first member, match it separately with the other members until the required selected-group size (r) is reached.
-
When every possible Combination for this first member is
exhausted, remove the current first member from the mother set.
The immediate next member becomes the new first member in the culminating set. - Take the first member in what is left of the mother set and repeat the same process from step II.
This is exactly what we will do with code to list up all
possible selections without repetition in Java.
Create a new Java project;
call it Miscellaneous
.
Create a new java class file;
call it Combination
.
Type out the adjoining Java code for the combination of different options
(nCr).
Why Bother About Combination
Well, isn't it obvious?
Say you are to pick only four (4) pupils from a class of six
- such a small class; our little Combination algorithm solves
this little problem for you by showing all your possible options
/ selection outcomes.
Java Code for Combination Class
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
public class Combination {
public List<String> words;
public int r; // min length of word
protected List<String[]> comb_store;
private int i;
public Combination() {
}
// point of entry
public List<String[]> possibleWordCombinations(List<String> candidates, int size) {
words = candidates;
r = size;
comb_store = new ArrayList<>();
i = 0;
// check for conformity
if (r <= 0 || r > words.size()) {
comb_store = new ArrayList<>();
} else if (r == 1) {
for (; i < words.size(); i++) {
comb_store.add(new String[]{words.get(i)});
}
} else {
progressiveCombination();
}
return comb_store;
}
// do combinations for all 'words' element
private void progressiveCombination() {
// single member list
repetitivePairing(Arrays.asList(words.get(i)), i + 1);
if (i + r <= words.size()) {
// move on to next degree
i++;
progressiveCombination();
}
}
// do all possible combinations for 1st element of this array
private void repetitivePairing(List<String> prefix, int position) {
List<String>[] auxiliary_store = new List[words.size() - position];
for (int j = 0; position < words.size(); position++, j++) {
// check if desired -- r -- size will be realised
if (r - prefix.size() <= words.size() - position) {
auxiliary_store[j] = new ArrayList<>();
auxiliary_store[j].addAll(prefix);
auxiliary_store[j].add(words.get(position));
if (auxiliary_store[j].size() < r) {
// see to adding next word on
repetitivePairing(auxiliary_store[j], position + 1);
} else {
comb_store.add(auxiliary_store[j].toArray(new String[0]));
}
}
}
}
}
Main Class
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
public class Miscellaneous {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> goods = new ArrayList<>();
goods.add("Eno");
goods.add("Chidi");
goods.add("Olu");
goods.add("Ahmed");
goods.add("Osas");
goods.add("Gbeda");
Combination combo = new Combination();
List<String[]> result = combo.possibleWordCombinations(goods, 4);
System.out.println(combo.words + " combination " + combo.r + ":\n");
int i = 0;
for (String[] set : result) {
System.out.println(++i + ": " + Arrays.toString(set) + ";");
}
System.out.println("\nNumber of ways is " + result.size() + ".");
}
}